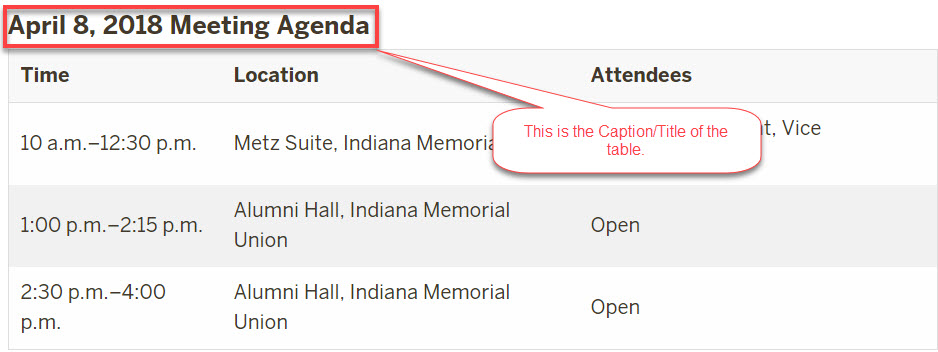
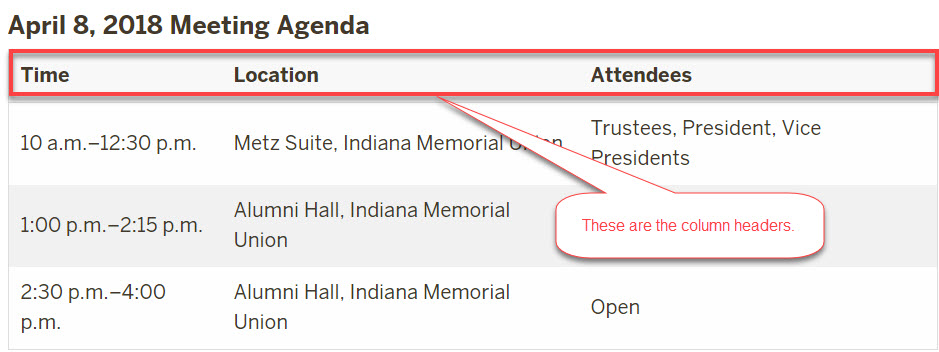
Use the Table chunk to create a table automatically. It is not advisable to use tables to manipulate the look of a page, they must be used for displaying data.
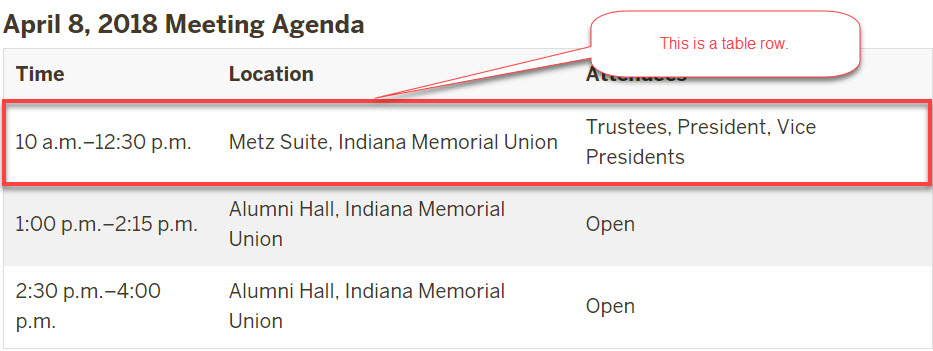
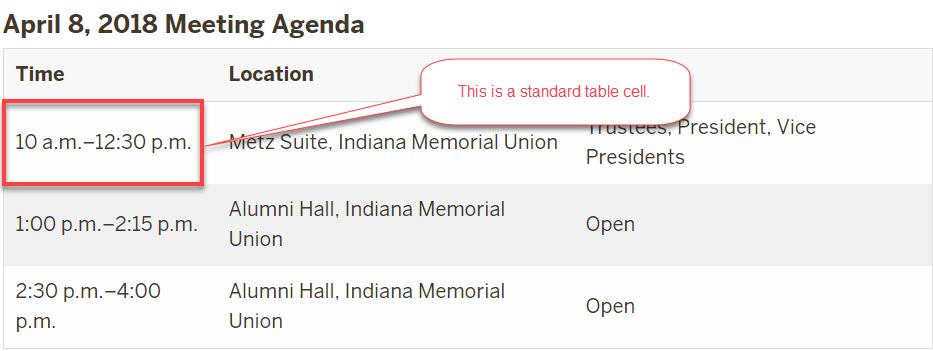
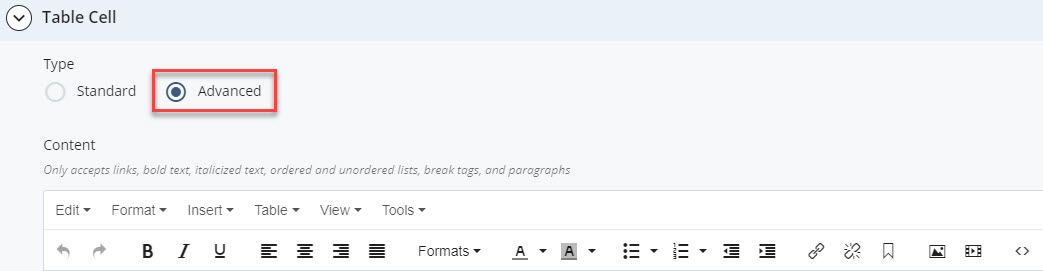
Use the table chunk to create a table that is automatically formatted for accessibility. You can use text (regular, bold, or italicized), links, lists, and paragraphs or break tags in a table.
The Table chunk will:
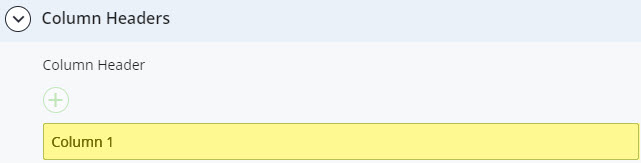
- Create simple tables with column headers
- Allow a maximum of five columns
- Allow links, bold/italicized text, paragraphs, and ordered/unordered lists in table cells
The Table chunk will not create:
- Complex tables with row spans and column spans
- Tables within tables
- Tables within accordion folds
- Tables with both column and row headers